https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/28695222
Abstract
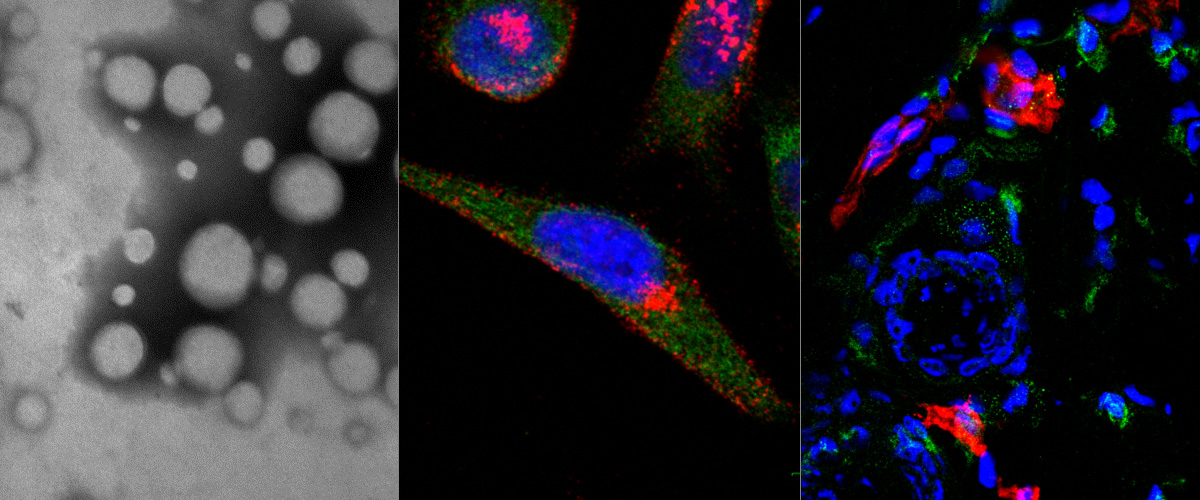
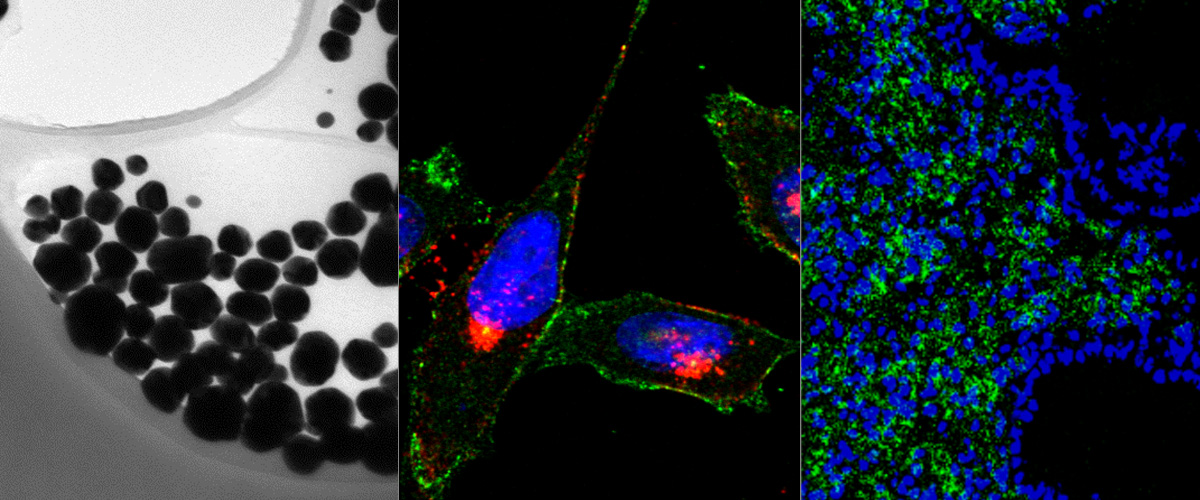
Attaching affinity ligands to nanoparticles (NPs) increases selectivity for targeting cells and tissues, and can result in improved sensitivity and reduced off-target toxicity in diagnostic and therapeutic systems. The decision over key features - NP size, shape, coating strategies and targeting ligands for clinical translation is often hampered by a lack of quantitative in vivo NP homing assays. Sensitive, internally controlled assays are needed which allow for quantitative comparisons (auditions) among various formulations of targeted NPs. We recently reported the development of peptide-functionalized, isotopically-barcoded silver NPs (AgNPs) for ultrasensitive studies centered on measuring relative ratios of NP internalization into cultured cells. Here we evaluated the application of this technology for NP homing studies in live mice using peptides with previously described tissue tropism; one peptide that favors vascular beds of the normal lungs (RPARPAR; receptor neuropilin-1, or NRP-1) and another that is selective for central nervous system vessels (CAGALCY). Equimolar mixtures of the peptide-targeted Ag107-NPs and Ag109 control particles were mixed and injected intravenously. Distribution profiles of Ag107 and Ag109 in tissue extracts were determined simultaneously through inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (ICP-MS). Compared to non-targeted particles up to ∼9-fold increased lung accumulation was seen for RPARPAR-OH AgNPs (but not for AgNPs functionalized with RPARPAR-NH2, which does not bind to NRP-1). Similarly, AgNPs functionalized with the brain-homing CAGALCY peptide were overrepresented in brain extracts. Spatial distribution (mapping) analysis by laser ablation ICP-MS (LA-ICP-MS) was used to determine the ratio Ag107/Ag109 in tissue cryosections. The mapping demonstrated preferential accumulation of the RPARPAR-AgNPs in the perivascular areas around pulmonary veins, and CAGALCY AgNPs accumulated in discrete areas of the brain (e.g. in the vessels of cerebellar fibrillary tracts). Based on these results, the internally controlled ratiometric AgNP system is suitable for quantitative studies of the effect of targeting ligands on NP biodistribution, at average tissue concentration and distribution at the microscopic level. The platform might be particularly relevant for target sites with high local variability in uptake, such as tumors.