https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29544111
Abstract
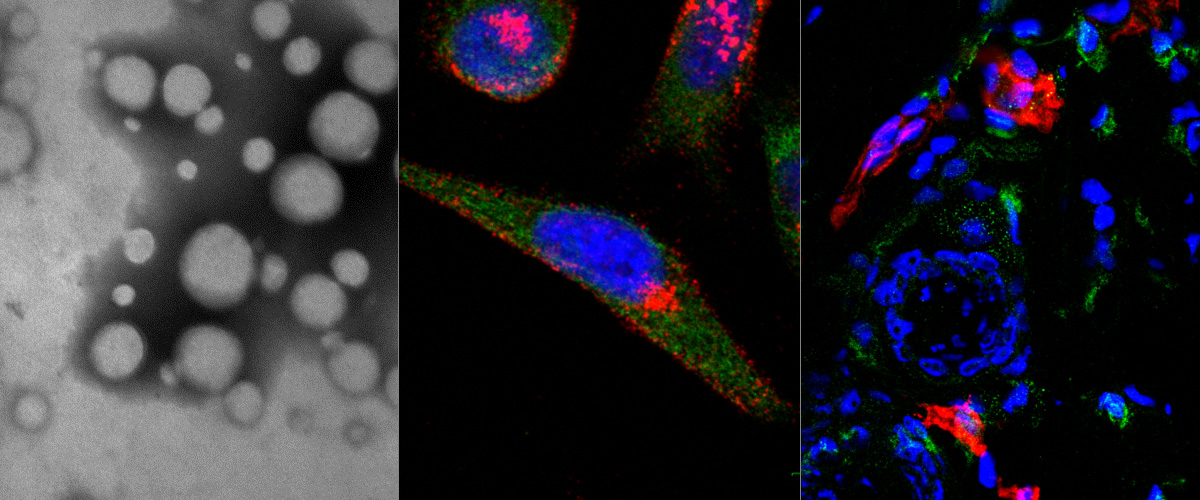
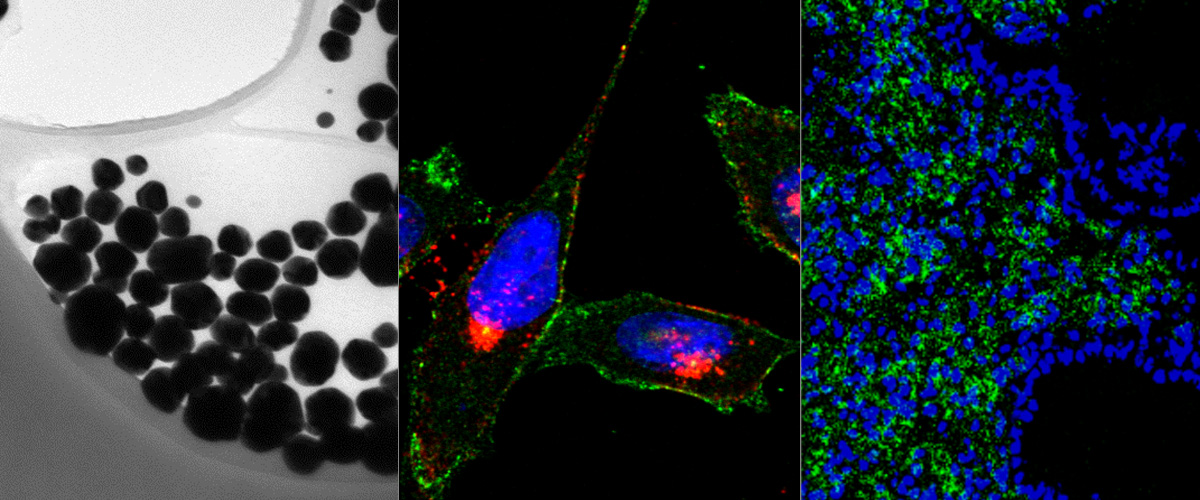
Cationic liposome-nucleic acid (CL-NA) complexes, which form spontaneously, are a highly modular gene delivery system. These complexes can be sterically stabilized via PEGylation [PEG: poly (ethylene glycol)] into nanoparticles (NPs) and targeted to specific tissues and cell types via the conjugation of an affinity ligand. However, there are currently no guidelines on how to effectively navigate the large space of compositional parameters that modulate the specific and nonspecific binding interactions of peptide-targeted NPs with cells. Such guidelines are desirable to accelerate the optimization of formulations with novel peptides. Using PEG-lipids functionalized with a library of prototypical tumor-homing peptides, we varied the peptide density and other parameters (binding motif, peptide charge, CL/DNA charge ratio) to study their effect on the binding and uptake of the corresponding NPs. We used flow cytometry to quantitatively assess binding as well as internalization of NPs by cultured cancer cells. Surprisingly, full peptide coverage resulted in less binding and internalization than intermediate coverage, with the optimum coverage varying between cell lines. In, addition, our data revealed that great care must be taken to prevent nonspecific electrostatic interactions from interfering with the desired specific binding and internalization. Importantly, such considerations must take into account the charge of the peptide ligand as well as the membrane charge density and the CL/DNA charge ratio. To test our guidelines, we evaluated the in vivo tumor selectivity of selected NP formulations in a mouse model of peritoneally disseminated human gastric cancer. Intraperitoneally administered peptide-tagged CL-DNA NPs showed tumor binding, minimal accumulation in healthy control tissues, and preferential penetration of smaller tumor nodules, a highly clinically relevant target known to drive recurrence of the peritoneal cancer.