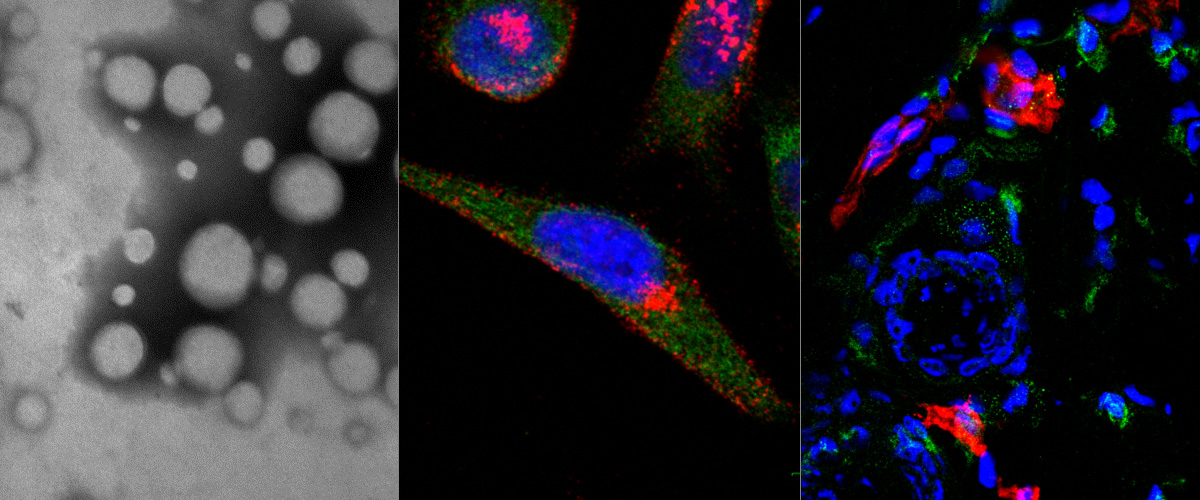
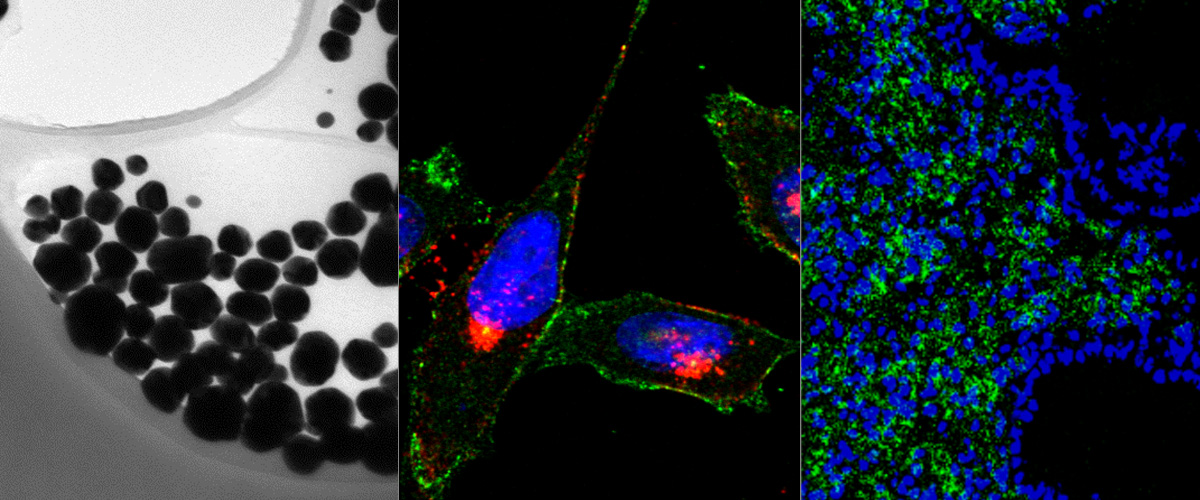
Homing Peptide-Based Targeting of Tenascin-C and Fibronectin in Endometriosis.
Success with our Estonian Research Council project "Precision targeting of infiltrative glioblastoma"
We are delighted to announce positive funding decision by the Estonian Research Council on our 5-year research project "Precision targeting of infiltrative glioblastoma". The project proposes studies on identification and preclinical validation of homing peptides able to penetrate the blood brain barrier and to target infiltrative glioblastoma cells. The project is expected to lead to identification and mechanistic characterization of the infiltrative glioblastoma targeting peptides and execution of the preclinical studies with peptide-guided therapeutic nanoparticles and radiotracers. These studies may lead to a new paradigm of peptide-based precision management of infiltrative glioblastoma.
Prof. Erkki Ruoslahti conferred the degree of Honorary Doctor of Biomedicine of UniTartu
Disntinguished professor Erkki Ruoslahti, a longtime mentor and present collaborator of Prof. Teesalu, has been conferred the degree of Honorary Doctor of Biomedicine of the University of Tartu for "cooperation with the University of Tartu in developing the research fields of cancer biology, nanomedicine and drug development".
Prof. Ruoslahti is a member of the US National Academy of Sciences since 1999 and has received several prestigious awards (e.g. Canada Gairdner International Award in 1997, Japan Prize in Cell Biology in 2005, and Albert Lasker Award for Basic Medical Research in 2022).
Adipose tissue identified as a frequent extrapulmonary site for SARS-CoV-2
The C-end Rule peptides, codiscovered by Prof. Tambet Teesalu, have emerged as important targeting and cellular entry elements for many viruses, including SARS-CoV-2. Our group participated in a collaborative study that demonstrated that adipose tissue is a frequent extrapulmonary site where SARS-CoV-2 can be found in COVID-19 patients and provided evidence that visceral fat cells are more susceptible than subcutaneous fat cells to SARS-CoV-2 infection in vitro. This study provides a mechanistic framework to help explain the exacerbated metabolic and inflammatory symptoms manifested by COVID-19 patients.
"SARS-CoV-2 infects adipose tissue in a fat depot- and viral lineage-dependent manner", Nat Commun. 2022; 13: 5722, published online 2022 Sep 29. doi: 10.1038/s41467-022-33218-8, https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9521555/
Prof. Teesalu delivers a COST Action CA17140 Seminar - "Development of homing peptides for precision guided delivery of nanoparticles"
Prof. Teesalu delivered a seminar "Development of homing peptides for precision guided delivery of nanoparticles" in the framework of the 7th Science and the Action seminar series.
Laboratory of Precision and Nanomedicine is an active member of the COST Action CA17140 - the first, pan-European interdisciplinary network of representatives from academic institutions and small and medium enterprises including clinical research organizations (CROs) devoted to the development of nanosystems carrying anticancer drugs from their initial design, pre-clinical testing of efficacy, pharmacokinetics and toxicity to the preparation of detailed protocols needed for the first phase of their clinical studies.
New nanosystem aimed at tumor-promoting macrophages reported in Cancer Research Communications (AACR)
In collaboration with the lab of Dr. Maria J. Vicent at the Principe Felipe Research Center in Valencia, Spain, we report development of a new peptide-guided nanosystem called "OximUNO". OximUNO, by removing the mannose receptor-positive macrophages from the tumor, was safe and effective in treating triple negative breast cancer in mice. OximUNO comprises a star-shaped polyglutamate (St-PGA) decorated with the CD206-targeting peptide mUNO that carries the chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin (DOX). In the TNBC model, a fluorescently labelled mUNO-decorated St-PGA homed to CD206+ TAMs within primary lesions and metastases. OximUNO exhibited no acute liver or kidney toxicity in vivo. Treatment with OximUNO reduced the progression of primary tumour lesions and pulmonary metastases, significantly diminished the number of CD206+ TAMs and increased the CD8/FOXP3 expression ratio (indicating immunomodulation). Our findings suggest the potential benefit of OximUNO as a TAM-depleting agent for TNBC treatment. Importantly, our studies also represent a novel design of a peptide-targeted St-PGA as a targeted therapeutic nanoconjugate.
Paper:
https://aacrjournals.org/cancerrescommun/article/doi/10.1158/2767-9764.CRC-22-0043/704874/Depletion-of-Mannose-Receptor-Positive-Tumor
Media:
https://meditsiiniteadused.ut.ee/en/node/139971?fbclid=IwAR0WNBefobanP8t1-pN20NuZKtWPx8tvvZjducvYL52GYhRNysDeUullKUs
https://tervis.postimees.ee/7544640/uus-ravim-voimaldab-tulevikus-loodetavasti-ravida-agressiivset-rinnavahki-edukamalt
https://novaator.err.ee/1608629164/vaike-valgujupp-muutis-vahiravimi-tappisrelvaks
https://www.eurekalert.org/news-releases/956479
CendR-driven cellular entrance of SARS-CoV-2 virus further decoded in a collaborative study
Our recent publication in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (PNAS) explains how the SARS-CoV-2 coronavirus can hijack an intracellular pathway to increase its infectivity. In collaboration with researchers at the University of Bristol (Dr. Boris Simonetti, Dr. Peter Cullen, Dr. Yohei Yamauchi), we studied how the SARS-CoV-2 and other viruses use the host intracellular machinery to enter into the cells. We previously showed that neuropilin-1 (NRP-1) is a co-receptor of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and that the binding to NRP-1 through the specific CendR motif displayed on the spike protein facilitates the cellular entry an infectivity of the virus. In this new study, we show how the NRP-1 and its ligands (nanoparticles displaying the CendR motif) are intracellularly transported by the ESCPE-1 protein complex. Knocking down essential proteins of the ESCPE-1 complex significantly decreased the internalization of the nanoparticles and, importantly, the infectivity of the corona virus. These findings could serve to develop new therapeutics that can interfere with the ESCPE-1 complex and prevent the NRP-1-mediated infection of the SARS-CoV-2 virus and other viruses.
Media:
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2022/06/220614095546.htm
Continued success in Euronanomed grant applications: ECM-CART project funded.
We are pleased to announce that our success in applying for Euronanomed grants continues. In November of 2021 it was announced that application “LDL-like nanoparticles for CAR-T-based glioblastoma immunotherapy” by our consortium led by Dr. Pablo Hervella (Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria de Santiago de Compostela, Spain) was successful. This project will seek to demonstrate that the targeted delivery of exogenous antigens to the extracellular matrix (ECM) of brain tumors provides a safe and specific target for chimeric antigen receptor T- cell (CART) for glioblastoma (GBM) treatment.
PNAS perspective: a widespread relevance of C-end Rule peptides to infection by different viruses.
In November of 2020 our team participated in two high-profile studies in Science that demonstrated that as SARS-CoV2 coronavirus matures, an enzymatic event causes the virus to present a specific peptide motif (C-end Rule or CendR peptide), and makes it accessible to bind with a widely-expressed class of mammalian NRP receptors. These reports focused on experiments to rigorously demonstrate the link between SARS-CoV2 and NRP-1, and we did not have sufficient space to discuss what we see as a fascinating and impactful emerging theme, namely that the NRP-1 pathway appears to influence viral infections in a generalized and widely-applicable manner.
In the current PNAS Perspective entitled “A widespread viral entry mechanism: The C-end Rule motif-neuropilin receptor interaction”, together with Drs Giuseppe Balistreri and Yohei Yamauchi (virologists at University of Helsinki and Bristol, respectively) we outline data-driven hypothesis and “connect the dots” to suggest that it is possible (and, indeed, likely) that NRP plays a critical role in infectivity and spread of multiple human pathogenic viruses. This model is seemingly relevant for any virus whose life cycle includes processing by the furin family of proteases, and that list includes a wide range of viruses that pose significant global health concerns, such as Influenza H5N1, Ebola, Dengue, Zika, West Nile, Yellow fever virus, Human Immunodeficiency virus, Hepatitis B virus, and Human Papilloma Virus.
An essential therapeutic implication of this concept is that a generalized approach to elicit pharmacological interference with the CendR/NRP-1 axis may offer an opportunity to attenuate the infectivity of all of these viruses!
We continue working on development of the further insight into the CendR/virus axis.
Reference: Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, . 2021 Nov 16;118(49):e2112457118. A widespread viral entry mechanism: The C-end Rule motif-neuropilin receptor interaction. Giuseppe Balistreri, Yohei Yamauchi, Tambet Teesalu
Congratulations to our PhD students for prestigious prizes!
The fall of 2021 has been very successful for our PhD students - Valeria Sidorenko, Allan Tobi and Kristina Põšnograjeva received prestigious grants from the Foundation of University of Tartu.
Valeria received a memorial scholarship from Valda and Bernard Õun Memorial Foundation in the amount of 5000 euros for attending an international conference.
Allan received the Hilda and Harry Mägi stipend for the amount of 2000€ to support further research and studies.
Kristina received a stipend of 2500 euros from the memorial fund of Liisa Kolumbus that she will use to attend an international conference.
Congratulations to our talented PhD students!